
- #Postgresql alter table add constraint unique how to#
- #Postgresql alter table add constraint unique install#
- #Postgresql alter table add constraint unique upgrade#
The “ CREATE TABLE” message verifies that the “ college” table has been successfully created. Add columns such as std_id, teach_id, sport_date, and notes in this table: CREATE TABLE college( To drop unique constraints from a table, users must follow the syntax stated below: ALTER TABLE tbl_nameĭROP CONSTRAINT constraint_name UNIQUE (col_name) ĪLTER TABLE is a command in Postgres used to alter/modify a table, while “ DROP CONSTRAINT” is a clause that drops the existing unique constraint from the table.įirst, create a " college " table with the “ CREATE TABLE” statement. In the PostgreSQL database, the “ DROP CONSTRAINT” clause removes the rule or policy that is already set using the “ ADD CONSTRAINT” clause.
#Postgresql alter table add constraint unique how to#
How to DROP UNIQUE CONSTRAINT in PostgreSQL? Step 3: DROP UNIQUE CONSTRAINT in PostgreSQL.Step 2: ADD UNIQUE CONSTRAINT in PostgreSQL.How to DROP UNIQUE CONSTRAINT in PostgreSQL?.The content that illustrates the demonstration is as follows:
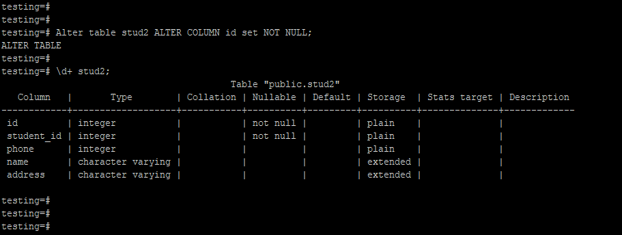
PostgreSQL's "DROP CONSTRAINT" clause with UNIQUE constraint is explained in this article. Using the DROP CONSTRAINT clause, users can drop any specific constraint, such as UNIQUE CONSTRAINT, FOREIGN KEY CONSTRAINT, CHECK CONSTRAINT, and so on. As a result, the system reports an error.In PostgreSQL, the “ DROP CONSTRAINT” clause is used with the ALTER TABLE statement to drop any specific constraint from a table. ALTER TABLE aa ENABLE CONSTRAINT aa_a1_check NOT VALID Įxecute the following statement to insert the values that do not meet the constraint. ALTER TABLE aa ENABLE CONSTRAINT aa_a1_check ĮRROR: check constraint "aa_a1_check" is violated by some rowĮxecute the following statement to enable the constraint but not to check whether the existing values meet the constraint. The system reports an error because a value in the table does not meet the constraint. INSERT INTO aa VALUES (10) Įxecute the following statement to enable the constraint and check whether the existing values meet the constraint. The value can be inserted because the constraint is disabled. ALTER TABLE aa ADD CONSTRAINT aa_a1_check CHECK(a1>10) DISABLE Įxecute the following statement to insert a value that does not meet the constraint. In this case, if the foreign key constraint is not disabled or deleted, the primary key constraint cannot be disabled.Įxecute the following statement to create a table: CREATE TABLE aa(a1 INT) Įxecute the following statement to create a constraint in which the values of the a1 column must be greater than 10. For example, a primary key constraint is referenced by a foreign key constraint of another table. Note A primary key constraint or a unique constraint may be referenced by other objects. The error includes the table data that does not meet the constraint. If the data does not meet the constraint, the system reports an error. By default, the system checks whether data in the table meets the constraint. ALTER TABLE table_name ENABLE CONSTRAINT constraint_name Įnables a constraint.The syntax supports the following four types of constraints: This indicates that this constraint does not apply to the data in the table and the data that is to be inserted to the table. The constraint_name constraint is in the disabled state. ALTER TABLE table_name ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name DISABLE Īdds a constraint to the table_name table.
#Postgresql alter table add constraint unique install#
You can execute the following statement to install the plug-in: CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS polar_constraint
#Postgresql alter table add constraint unique upgrade#
For more information about how to upgrade the kernel version, see Upgrade the minor version.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
